
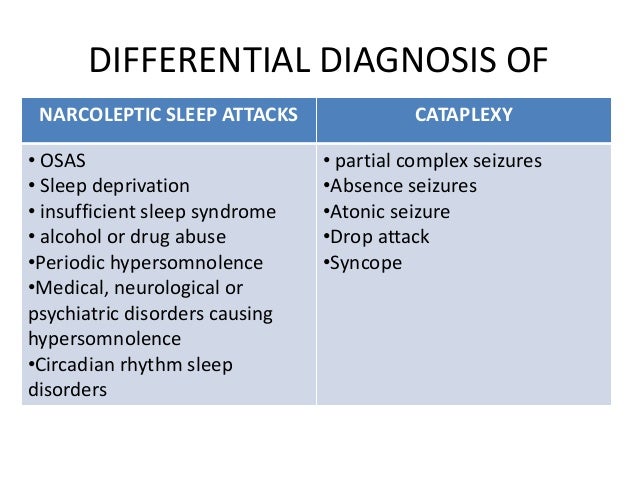
Cataplexy in particular is characterized by episodes that occur during moments of heightened emotion. The catatonia rating scale may be helpful in assessments. Narcoleptic and cataplectic episodes can last from several seconds up to 30 minutes, and often will take place when the cat is eating, playing, excited, or is engaging in sexual activity. Patients may develop hyperthermia, tachycardia, and hypertension and be in danger of collapse from exhaustion. There is also an excited-delirious variety of catatonia with extreme hyperactivity (constant motor unrest or non-purposeful repetitive motor activity). Other features include mitgehen (eg, arm raising in response to light finger pressure, despite instructions to the contrary), echopraxia, echolalia or verbigeration (repetition of phrases or sentences like a scratched record) or stereotypies (repetitive meaningless activities). There may be automatic obedience or exaggerated co-operation, combativeness, or even ambitendency (alternating co-operation and opposition). Typically, cataplexy does not develop for months or even years after the first signs of excessive daytime sleepiness, but in rare cases it is the first observed. Negativism - involuntary resistance to passive movement, or involuntary oppositional behaviour (Gegenhalten). catalepsy cataplexy kat- uh-plek-see noun a condition characterized by sudden, brief attacks of muscle weakness sometimes causing the body to fall helplessly, that is usually triggered by strong emotion: often associated with narcolepsy.Mutism - verbally minimally responsive.Motoric immobility - catalepsy (see below), waxy flexibility, stupor (extreme hypoactivity, minimal response to stimuli, including painful ones).Note whether there are any neurological signs or abnormal movements, or cogwheel rigidity (Parkinsonism). The condition is most commonly associated with. Check for a pyrexia, meningism or other signs of infection. Cataplexy is a sudden, brief loss of voluntary muscle tone triggered by strong emotions such as laughter. Hepatic failure or chronic kidney disease.Electrolyte imbalance, hyperparathyroidism.Addison's disease, hypopituitarism, carcinoid tumours.Substance intoxication or drug withdrawal.Pervasive developmental disorders, including autism.

Catalepsy is a nervous condition characterized by seizure or trance along with loss of sensation and muscular rigidity. Cataplexy is a condition of sudden muscle weakness triggered by strong emotions such as laughing and excitement. Degenerative neurological diseases, including multiple sclerosis and Huntington's disease. Cataplexy and catalepsy are two types of disorders that cause muscle rigidity and loss of sensation over pain and touch.Tumours and other intracranial lesions (including post-surgery).Cerebrovascular disease (thrombosis or haemorrhage, venous thrombosis, etc).Non-convulsive status epilepticus, complex partial seizures.Submitted comments are subject to editing and editor review prior to posting.Read any comments already posted on the article prior to submission. Submit only on articles published within 6 months of issue date.(Exception: original author replies can include all original authors of the article) Submissions should not have more than 5 authors.Reference 1 must be the article on which you are commenting. Submissions must be You (and co-authors) do not need to fill out forms or check disclosures as author forms are still valid If you are responding to a comment that was written about an article you originally authored: Your co-authors must send a completed Publishing Agreement Form to Neurology Staff (not necessary for the lead/corresponding author as the form below will suffice) before you upload your comment. You must have updated your disclosures within six months:
#Catalepsy vs cataplexy free
In drug nave patients (74), catalepsy free days/week changed from 0 at start of the. Catalepsy is the sudden loss of voluntary muscle control caused by severe fatigue, stress, or a strong emotion like laughter, anger or fear. If you are uploading a letter concerning an article: often with periods of brief involuntary sleep and/or cataplexy.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
